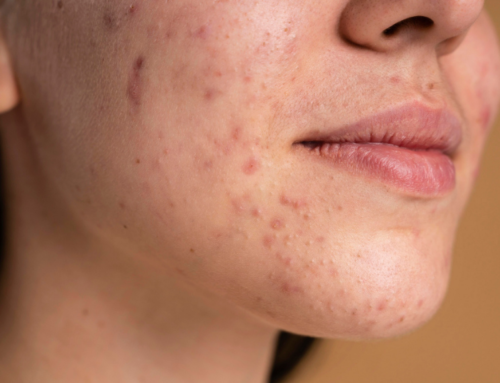
What is melasma?
Melasma is characterized by irregular, dark, hyper-pigmented patches that occur symmetrically on both sides of the face.
It is typically found in the below areas
- Cheeks
- Forehead
- Bridge of the nose
- Above the upper lip
- Chin
As the pigmented patches resemble the shape of a butterfly, this condition is also referred to as the “The Butterfly Mask”. Rarely melasma may occur on other parts of body like neck and forearms.

Who gets melasma?
While melasma can affect both men and women, it is primarily seen in women. It is found in the age group of 20 to 50 yrs. People with darker skin are more likely to get melasma because they have more active melanocytes than those with lighter skin. People with a family history are much more likely to get melasma.
What are the types of melasma?
- Epidermal melasma – in this type there is presence of excess melanin in the superficial layers of skin.
- Dermal melasma – is characterized by the presence of melanophages (cells that ingest melanin).
- Mixed melasma – includes both the epidermal and the dermal type.
- Deep dermal melasma – is characterized by excess melanocytes and is commonly found in dark skinned people.

What causes melasma?
Melasma is caused when the pigment-producing-cells called the melanocytes become overactive and secrete excess melanin. The excess melanin gets deposited in the outer layer of the skin causing the appearance of dark patches on the surface. It is caused by a varying combination of factors like –
A change in hormones – Melasma could be triggered by hormonal changes like pregnancy, menopause and hormone replacement therapy. The pregnancy induced melasma is called chloasma or the mask of pregnancy and is largely caused due to high levels of progesterone. People suffering from thyroid disease or polycystic ovarian disease also have a greater chance of developing this condition.
Genetic – People with a genetic predisposition are at an increased risk of developing melasma. Skin pigmentation is originally caused by the UV rays from the sun. Normally the skins natural protection is able to resist the UV rays, but as people grow older, the immunity of the body reduces. This makes it possible for the years of accumulated sun exposure to take its toll on the skin. When this happens, it causes some genetic mutations of the genes that are responsible for the formation of skin color melanin. The genetic mutation experienced in such people can be passed on to their offspring’s and the cycle continues.
Sun exposure – ultraviolet light from the sun stimulates the melanocytes. Even a minimal amount of sun exposure can make melasma relapse. Most people find their melasma worsening in summer.
Stress – Recent research has established a link between stress and melasma. Stress can activate the propriomelanocortrin gene that prompts the cells to produce more pigment.
Cosmetics – skin care products that irritate the skin may trigger or worsen melasma.

What is the psychological impact of Melasma?
Melasma often has serious psychological effects on the persons self esteem. Some sufferers avoid social contacts with friends and family as they feel ashamed of their skin.
People with Melasma hold strong negative emotions about their condition, some feel disfigured and embarrassed. They become conscious while interacting with people as they feel that other people are focusing only on their skin. Emotional depression is common among those who have very severe Melasma or who have suffered for long periods of time. Some have a sense of hopelessness that their condition will never be cured.
How is melasma diagnosed?
Melasma can be easily recognized by the characteristics of the pigmentation and its distribution on the face. A woods lamp examination is used to determine the depth or the number of layers that are affected by melasma.
How is melasma treated?
Treating Melasma is not like treating just any other form of pigmentation. When it comes to treating Melasma, it is recommended to avoid overly-aggressive treatments. The common notion is that an acid peel or a laser therapy will just peel off the pigmentation from the skin surface leaving behind a fair and glowing skin. However, irritation due to procedures like chemical peels and derma-abrasions can only make Melasma worse. Melasma responds best to non-invasive methods.
External applications – For mild cases external applications consisting tyrosinase inhibitors are prescribed. They work by preventing pigment formation by inhibiting the formation of melanin by melanocytes. Apart from tyrosinase inhibitors, skin lightening agents also play an important role in fading away the patches.
Oral medication – Melasma patch is not like a banana skin that can be just peeled off from the surface. It is a much more stubborn, deep-seated pigmentation and is caused due to an overactive cell underneath which secretes excess melanin. Stabilizing this overactive cell is crucial in treating melasma. Oral medicines work by reducing the activity of the pigment producing cells. For severe cases a combination approach is generally more effective.
Sun protection – For those who suffer from sun allergies, a broad spectrum sunscreen usage is important for successful management of Melasma.
During the treatment, it is important to adhere to the three Ps for maximum results – Patience, Persistence and Precaution. Patience is necessary as melasma can be slow to respond to treatment, especially if it has been present for a long time. Persistence is necessary in the form of ongoing skin care to maintain the results of the treatment and prevent relapses. Precaution is the third important thing. Exposure to sun and harsh chemical peels need to be avoided as they trigger inflammation and worsen Melasma. Following the three Ps can help bring better results.

Dr. Pranjal Shamsher is the first Skin Doctor in Bangalore to offer natural, non-surgical and non-invasive treatments for skin disorders. With over 25 years of experience in the field Dermatology, Dr. Pranjal Shamsher has devised a unique Multi-Therapy approach involving the use of several therapies at the same, to treat the most stubborn, obstinate and long-standing skin disorders with a skin-friendly and 100% side-effect free results. Her integrated and Multi-Therapy approach has helped many chronic disease sufferers to recover safely without any side-effects.
Dr. Shahid Shamsher is one of India’s first certified Trichologist practicing in the field of Trichology for 27 years and is recognized as one of the Best Hair Doctor in Bangalore. He is the only Trichologist in India to be simultaneously certified from the U.K, Australia, and India.